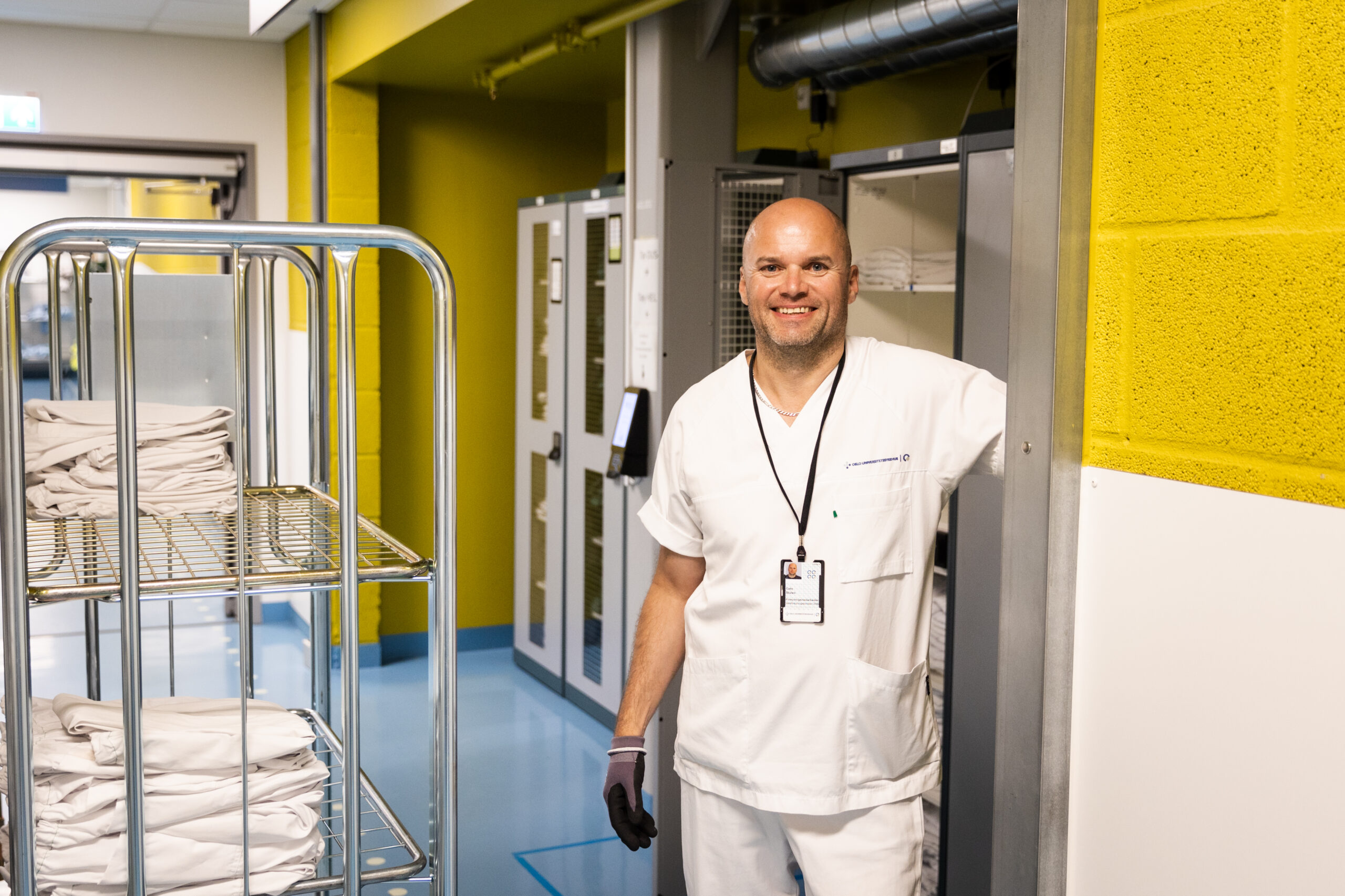
Sustainable Logistics in Healthcare Organizations
About the course
Target group
Health and care workforce
Key words
Course introduction
This course begins with a general introduction to the concepts of sustainability, logistics, and sustainable logistics. It then continues with a closer look at various logistical concepts that can be used on processes that healthcare workers engage in daily, before examining the differences between linear value chains and the circular economy. The focus is on waste and reverse logistics, as well as strategies for thinking about change. Working toward more sustainable processes requires change management, and the course provides some general tips on how to facilitate change within an organization. Finally, it offers an introduction to methods, and tools for driving continuous improvement in healthcare processes.
- Introduction to Sustainable Logistics in Healthcare Organizations
- Sustainable Logistics in Healthcare Organizations
- Linear vs. Circular Economy and Value Chains
- Waste Management and Reverse Logistics
- Change Management
Tools for Continuous Improvement
Details to know

Downloadable certificate
Share your certificate on Linkedin
Assessment
7 Quizzes
Learning outcomes
Module 1
- Competence
- Is able to describe the fundamental principles of sustainability and logistics and their intersection in health and care.
- Knowledge
- Knows the key concepts of sustainability and logistics and their relevance to health and care operations.
- Skills
- Explains the importance of sustainable logistics in improving efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
- Identifies key drivers behind the green transition in health and care logistics.
Module 2
- Competence
- Is able to apply logistical principles to enhance sustainability in health and care supply chains and inventory management.
- Knowledge
- Knows the role of logistics in health and care and how purchasing and inventory control affect sustainability.
- Skills
- Uses concepts like Economic Order Quantity, XYZ-analysis, and ABC-analysis to improve efficiency.
- Identifies strategies to optimise inventory control to reduce waste and environmental footprint.
Module 3
- Competence
- Is able to compare linear and circular economy models and evaluate their relevance for sustainable health and care logistics.
- Knowledge
- Knows the differences between linear and circular supply chains and their implications for sustainability.
- Skills
- Assesses the advantages of circular economy practices in health and care.
- Identifies key strategies for transitioning from linear to circular logistics models.
Module 4
- Cometence
- Is able to implement sustainable waste management and reverse logistics strategies in health and care settings.
- Knowledge
- Knows different forms of waste and their impact on health and care sustainability.
- Skills
- Identifies appropriate waste management and recycling methods.
- Explains how reverse logistics can improve sustainability outcomes in health and care.
Module 5
- Competence
- Is able to support and implement sustainable logistics initiatives using change management frameworks.
- Knowledge
- Knows the principles of change management and frameworks like ADKAR and Kotter’s 8-step model.
- Skills
- Applies change management strategies to implement sustainable logistics practices.
- Identifies barriers to change and develops solutions to facilitate organisational transitions.
Module 6
- Competence
- Is able to apply Lean and Value Stream Mapping techniques to improve sustainability in health and care logistics.
- Knowledge
- Knows the basics of Lean methodology and its application in logistics.
- Skills
- Uses Value Stream Mapping to identify inefficiencies and improve logistics processes.
- Develops continuous improvement strategies to enhance the sustainability of health and care logistics over time.
More detailed Learning Outcomes can be found in module introductions.
Introduction to Sustainable Logistics in Health Organizations
Lessons
Introduction 1. Introduction to Sustainable Logistics in Healthcare Organizations 2. Why the demand for a green transition in the healthcare sector ReferencesMore on Sustainable Logistics in Health Organizations
Lessons
Introduction 1. Diving Deeper Into Logistics And How Processes Might Be A Bit More Sustainable By Using Logistical Concepts ReferencesLinear vs. Circular Economy and Value Chains
Lessons
Introduction 1. From linear to circular logistics ReferencesWaste Management and Reverse Logistics
Lessons
Introduction 1. Waste management and return logistics ReferencesChange Management
Lessons
Introduction 1. Change Management ReferencesTools for Continuous Improvement
Lessons
Introduction 1. Practical tools for continuous improvement References Course Evaluation
Co-funded by the Erasmus+ programme of the European Union under Grant Agreement number 101056563.

Co-funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or EACEA. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.

