Water Management in Agriculture
About the course
Target group
Students, teachers, professionals, farmers and agroindustry
Key words
Course introduction
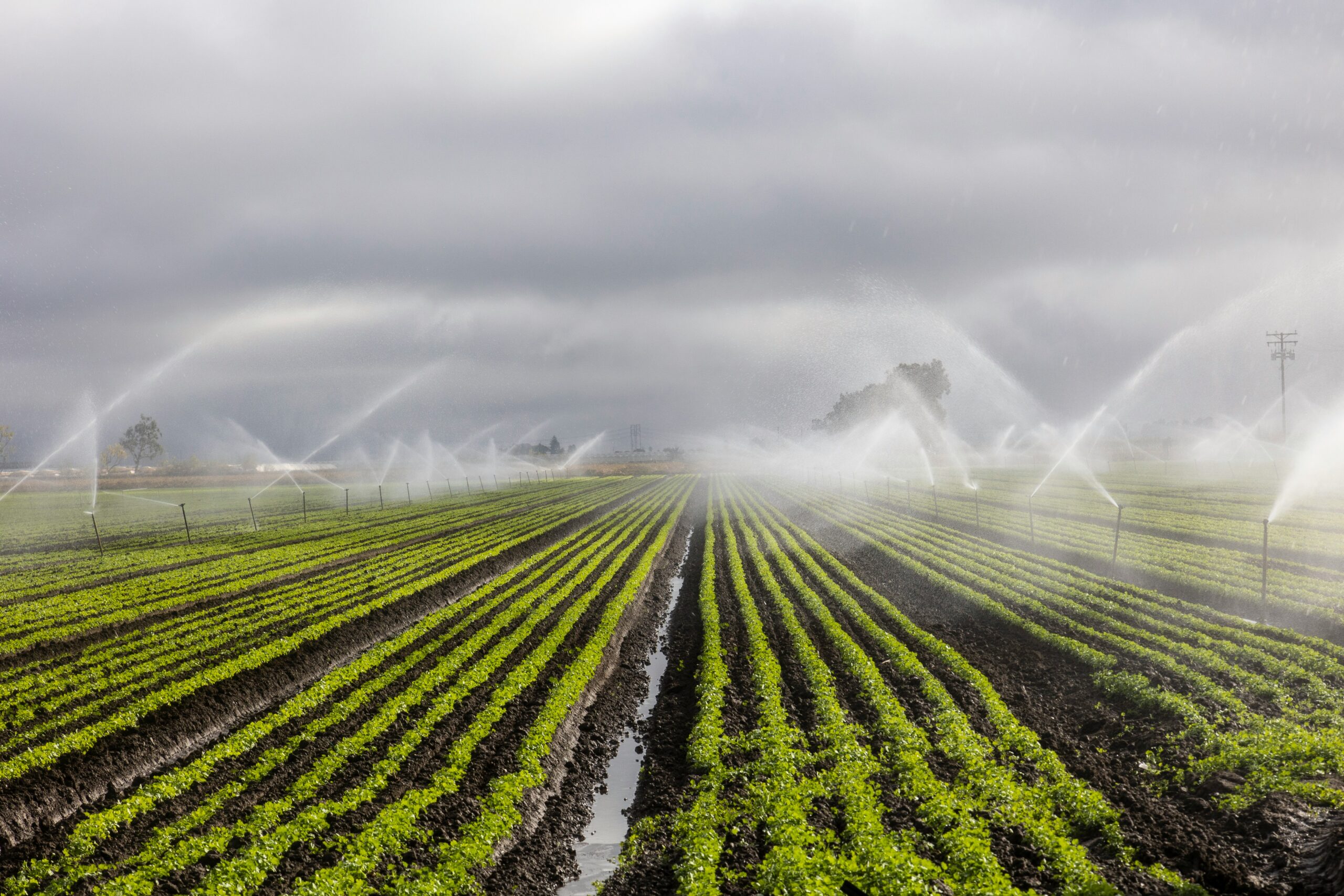
Module 1 explores the critical role of water in agriculture, covering its importance for crop growth, livestock, and ecosystem health. Water supports photosynthesis, nutrient uptake, and regulates temperature, influencing crop productivity. Agriculture consumes about 70% of global freshwater, with varying water needs depending on the crop and region. The module highlights different water sources—rainwater, surface water, and groundwater—and their use in irrigation, livestock, and aquaculture. It also addresses the impacts of water stress, irrigation methods, soil-water relationships, and the effects of climate change. Sustainable water management practices, such as efficient irrigation and rainwater harvesting, are emphasized for long-term agricultural resilience.
Module 2 focuses on sustainable water resource management in agriculture, covering efficient irrigation techniques, rainwater harvesting, groundwater recharge, and the use of treated wastewater. It addresses challenges like seasonal variability, climate change, and over-extraction, offering solutions for maintaining productivity while conserving water. Topics include surface water management, desalination, and innovative technologies for monitoring water availability. Case studies from regions like Israel, California, and Saudi Arabia highlight practical applications. Policies and integrated management strategies like IWRM are also explored, providing a comprehensive understanding of how to balance agricultural needs with environmental sustainability.
Module 3 examines the challenges in agricultural water management, focusing on issues such as overdependence on rainfall, mismanagement of irrigation, and fragmented water rights. It explores the impact of poor irrigation infrastructure, seasonal water scarcity, and soil-water dynamics, leading to inefficiencies and increased water demand. Other barriers include limited access to affordable technology, unsustainable crop choices, and industrial-urban water competition. The module also highlights the decline of traditional water management systems, lack of farmer training, and the water-energy nexus. It emphasizes the need for better governance and integrated policies to address these complex, interrelated challenges.
Details to know

Downloadable certificate
Share your certificate on Linkedin
Assessment
9 Quizzes
Learning outcomes
Ace-Ex U-1 Circular economy principles:
- 1.1: Communication and implementation of principles
- 1.2 Raising awareness and facilitating knowledge-sharing
Ace-Ex U-2 Innovation management:
- 2.1: Innovation and implementation of practices
Ace-Ex U-4 Technical skills:
- 4.1: Implementing circular economy practices
- 4.3: Water management
- 4.6: Life cycle assessment
- 4.7: Waste management
Ace-Ex U-5 Regulatory frameworks:
- 5.4: Adopting circular economy practices
More detailed Learning Outcomes can be found in module introductions.
Fundamentals of Water Management in Agriculture
Lessons
Introduction 1. The Role of Water in Agriculture 2. Water Resources for Agriculture 3. Challenges in Agricultural Water Management ReferencesTechniques and Technologies in Water Management
Lessons
Introduction 1. Water in the Agricultural Soil Physics and Chemistry 2. Irrigation Systems 3. ReferencesSustainable Water Management Practices
Lessons
Introduction 1. Water Balance 2. Conservation Practices for Water Efficiency 3. Climate Change Adaptation in Water Management References Course Evaluation
Project nr. 101110547.

Co-funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or EACEA. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.

