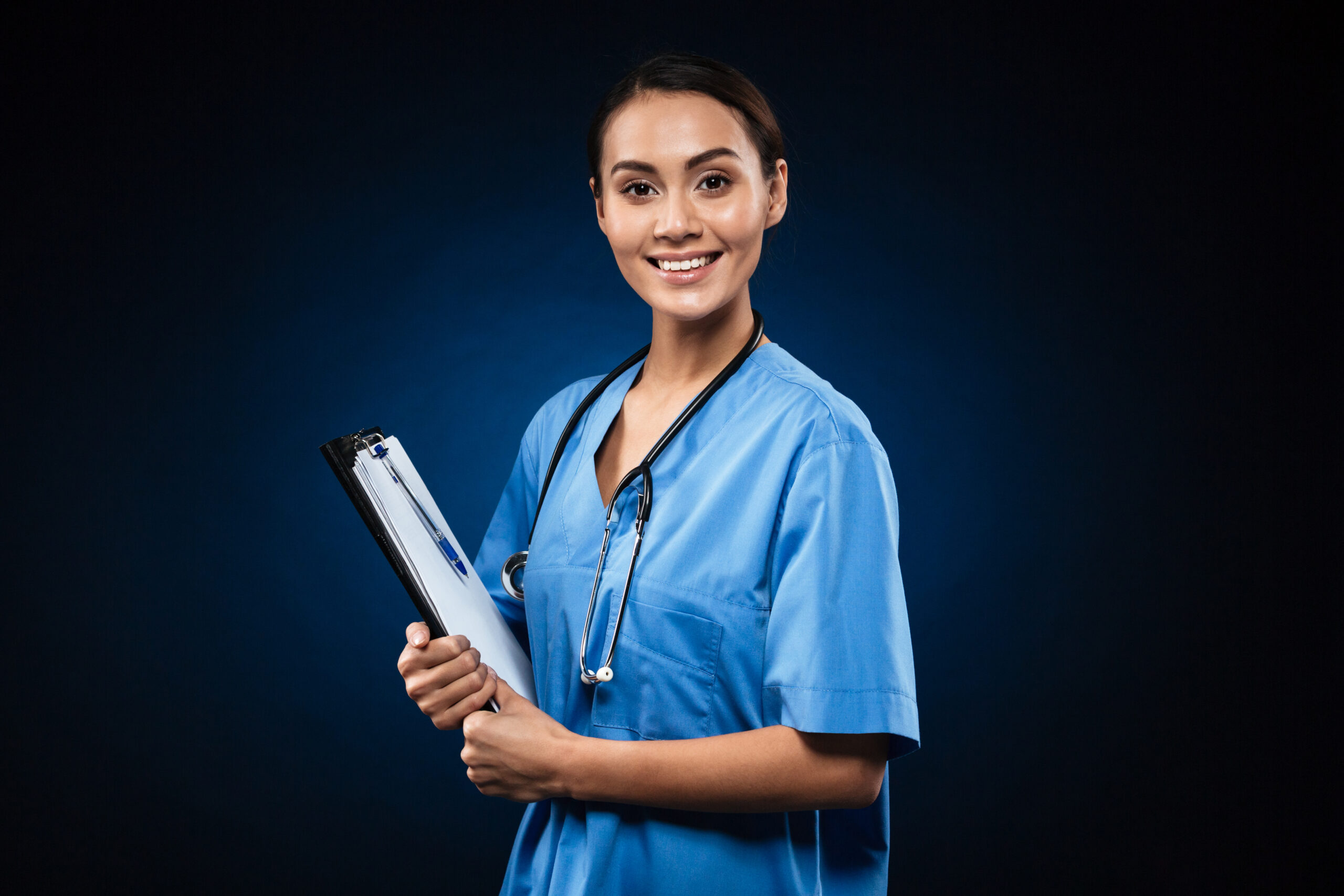
Digital Care Coordinator
About the course
Target group
Nurses, Specialist Nurses, Nursing Assistants, Nursing Aides
Key words
Course introduction
The concept of care coordination is not new. Nurses seem to have known its importance for a long time. In the context of collaboration driven by the needs and preferences of patients and their families, the nurse is essential to the quality of care, the efficient use of healthcare resources, and, most importantly, the well-being of patients.
Nurses are a key pillar in the care coordination process as they improve patient health outcomes, promote effective multidisciplinary, interprofessional collaboration, and help reduce healthcare costs.
The Care Coordinator (Nurse) course is designed to provide nurses with the skills and knowledge they need to effectively manage and coordinate patient care in a variety of healthcare settings. The course addresses the multi-faceted role of the care coordinator and emphasises the importance of holistic patient-centered care. Key topics such as care management, patient advocacy, and interdisciplinary collaboration are covered, as well as the essential elements necessary to ensure seamless care transitions and improve patient outcomes.
During the course, participants will be taught how to assess patient needs, develop individualized care plans, and coordinate health care providers. The module addresses critical aspects of care coordination such as chronic disease management and the integration of resources to support the long-term patient health and well-being, the importance of communication with both patients and the health care team to ensure that the health care is delivered in a timely and efficient manner.
Details to know

Downloadable certificate
Share your certificate on Linkedin
Assessment
8 Quizzes
Learning outcomes
Module 1
- Competence
- Is able to implement care coordination strategies to enhance patient outcomes and improve health and care systems efficiency.
- Knowledge
- Knows the role of care coordination in reducing health and care costs and improving patient experience.
- Understands the key responsibilities of nursing care coordinators in facilitating communication between patients and health and care professionals.
- Skills
- Assesses the impact of care coordination on patient safety, quality of care, and hospital readmissions.
- Implements strategies to enhance interdisciplinary collaboration and care continuity.
- Identifies team roles and responsibilities to optimise collaboration.
- Develops communication frameworks to improve patient-provider interactions.
- Utilises digital tools to streamline care documentation and patient follow-ups.
Module 2
- Competence
- Is able to facilitate care coordination activities in community health and care settings, ensuring effective communication and resource utilisation.
- Knowledge
- Knows the responsibilities of nurse care coordinators in bridging communication between patients and health and care teams.
- Understands the role of nurse leaders in fostering interprofessional collaboration to streamline care processes.
- Knows how to manage chronic health problems within a coordinated care approach.
- Skills
- Develops structured approaches for patient follow-up and support.
- Implements community outreach initiatives to improve care accessibility.
- Facilitates teamwork among health and care professionals to enhance service delivery.
- Uses digital tools and technologies to support community-based care coordination.
- Establishes interdisciplinary protocols to improve patient care pathways.
- Develops long-term management plans for chronic disease patients.
- Monitors patient progress to prevent complications and hospital readmissions.
- Engages with patients and caregivers to promote self-management strategies.
Module 3
- Competence
- Is able to coordinate patient-centred care strategies for complex and specialised health conditions, ensuring seamless transitions between hospitals, primary health and care, and specialised care settings.
- Knowledge
- Knows the essential functions and responsibilities of care coordinators in various specialised clinical settings.
- Understands best practices for effective communication and collaboration among health and care providers.
- Knows how to assess the effectiveness of care coordination activities in optimising health services and reducing hospital readmissions.
- Understands the principles of facilitating seamless transitions of care between different health and care settings.
- Skills
- Assesses patient needs and develops tailored care plans.
- Implements evidence-based interventions for high-risk patients.
- Coordinates with specialists to ensure continuity of care.
- Applies structured communication methods to enhance care transitions.
- Ensures continuity of care through integrated service models.
- Facilitates case discussions and collaborative decision-making among multidisciplinary teams.
- Uses quality metrics and patient feedback to improve care strategies.
- Evaluates health and care resource utilisation and makes recommendations for efficiency improvements.
- Coordinates discharge planning and follow-up care to support patient recovery.
- Engages multidisciplinary teams to ensure smooth patient transitions and reduce readmissions.
- Implements early intervention strategies to minimise patient deterioration post-discharge.
More detailed Learning Outcomes can be found in module introductions.
Introduction to Care Coordinator (Nurse)
Lessons
Introduction 1. What is Care Coordination? 2. Coordination's Strategies ReferencesCare Coordinator's Activities in Community Settings
Lessons
Introduction 1. Care Coordinator in Palliative Care 2. Care Coordinator in Elderly Care 3. Care Coordinator in Vulnerability Care ReferencesCare Coordinator's Activities in Clinical Settings
Lessons
Introduction 1. Care Coordinator in Mental Health Care 2. Care Coordinator in Acute Stroke Care 3. Care Coordinator for Patients with HIV References Course Evaluation
Co-funded by the Erasmus+ programme of the European Union under Grant Agreement number 101056563.

Co-funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or EACEA. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.

